Traditional Treatmnents
Traditional treatments for erectile dysfunction
Many men prefer non-invasive erectile dysfunction treatments; however, all management options should be carefully evaluated.
The American Urological Association suggests that any possible treatment may be used as a first-line therapy. Moreover, the partner’s disposition to try different treatment options has been demonstrated to increase the likelihood of sexual function recovery.
If no organic causes can be found for erectile dysfunction, psychological counseling could be an effective option, and if other morbidities are involved (for example, cardiovascular problems) erectile dysfunction treatment should include their management too.
Erectile dysfunction-specific treatment options can be divided into traditional and novel approaches. In particular, traditional treatments include lifestyle changes, topical or oral medications, intracavernosal injections, intraurethral suppositories, vacuum-assisted erectile devices, and surgically implantable prostheses.
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes can both prevent progression and improve regression of early erectile dysfunction manifestations. Effective approaches include physical activity, weight loss, reducing caloric intake, improving diet, and quitting smoking. However, they are a simple solution only in theory; in fact, they are the most difficult to execute.
Oral medications
Oral medications act on the mechanism of erection; that is why an intact nervous system pathway is needed for their functioning. They are taken by mouth prior to intercourse: sildenafil and vardenafil, which should be taken on an empty stomach, are used on an as-needed basis; tadalafil, which lasts longer in the body and is not affected by food, is approved for daily use.
For oral medications to work some sexual stimulation is needed. If nerves for erection are damaged, they may not be as effective. That is why they cannot work as desired, for example, in men with severe diabetes or that have undergone radical prostatectomy. Moreover, they are contraindicated to men taking nitrates, they should be taken with caution by men already in therapy with alpha-receptor-blocking medications, some men have difficulties timing on-demand ones, and others find this drugs cost-prohibitive.
Oral medications for erectile dysfunction, particularly on-demand ones taken at high dose, are not side effects-free. Among others, some controversy pointed to the melanoma skin cancer or prostate cancer risk associated to the treatment with this drugs; however, there is no evidence to confirm this association.
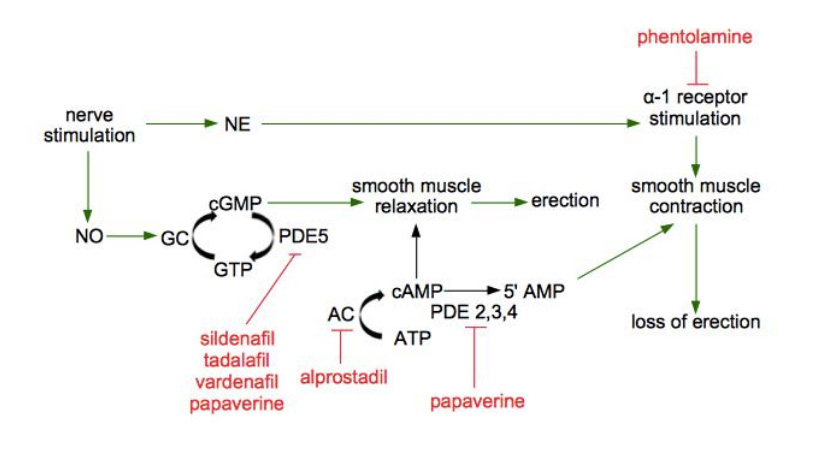
The mechanism of erection and of drugs for erectile dysfunction. Adapted from Krzaztek SC et al, 2019. AC, adenylyl cyclase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; GC, guanylate cyclase; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; NE, norepinephrine; NO, nitric oxide; PDE5, phosphodiesterase type 5; PDE5i, phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PDEi, phosphodiesterase inhibitor; PGE1, prostaglandin E1.
Intracavernosal injections
Intracavernosal injections represent a more invasive treatment consisting in the injection of a medicine (in most cases, alprostadil) in the lateral base of male organ. Alprostadil is also commonly combined with papaverine or phentolamine, or both. They are preferred in men in whom oral medications are contraindicated or that do not tolerate them because of their side effects, and in men with damaged erection nerves. Conversely, they are contraindicated in men with a history of recurrent priapism, Peyronie’s disease, and bleeding disorders.
Alprostadil is available as intraurethral suppositories too. However, this option is associated to side effects such as pain, and should be used with caution in men with urethral disease or increased priapism risk. Finally, it can be administered also via topical cream.
Vacuum-assisted erectile devices
Vacuum-assisted erectile devices pump blood to cause erection. They are effective in 90% of men, but their use may be challenging for men with decreased skill in performing tasks with the hands or with large amount of lower abdominal fat. Moreover, their long-term use decreases because of psychological difficulties, pain and sensation changes. Finally, caution should be taken by men on blood thinners because of the risk of bruising.
Surgically implantable prostheses
Surgically implantable prostheses use is associated with higher satisfaction rate than oral medications and intracavernosal injections, but they are typically reserved for men who do not responded to less invasive approaches. They include malleable devices that remain rigid and may be simply positioned, good for men with limited skill in performing tasks, and inflatable devices connected to a pump and to a fluid reservoir placed in the body, that require men squeezes the pump to pull the fluid in the prostheses to achieve the erection; all is needed to return to the flaccid state is pushing a button. Inflatable devices erection is more physiologic-appearing than malleable devices one.

